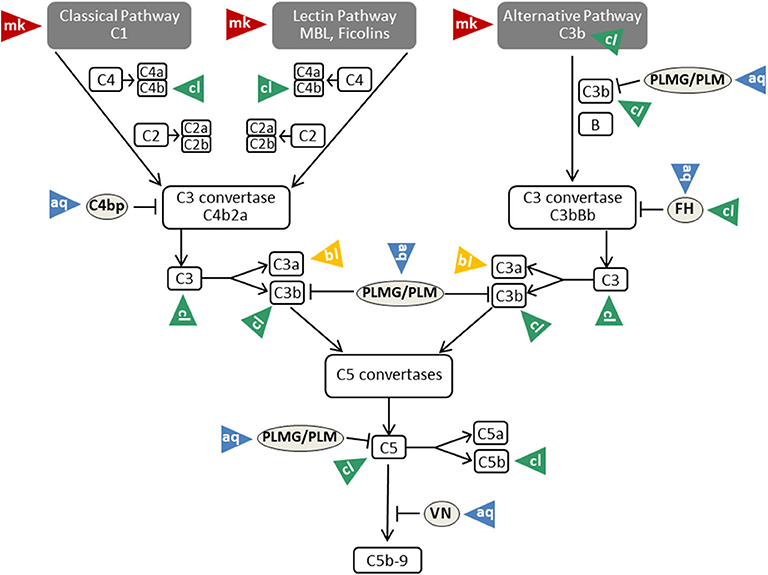
Effects of LL-37 and the main products of SAP-dependent degradation of... | Download Scientific Diagram
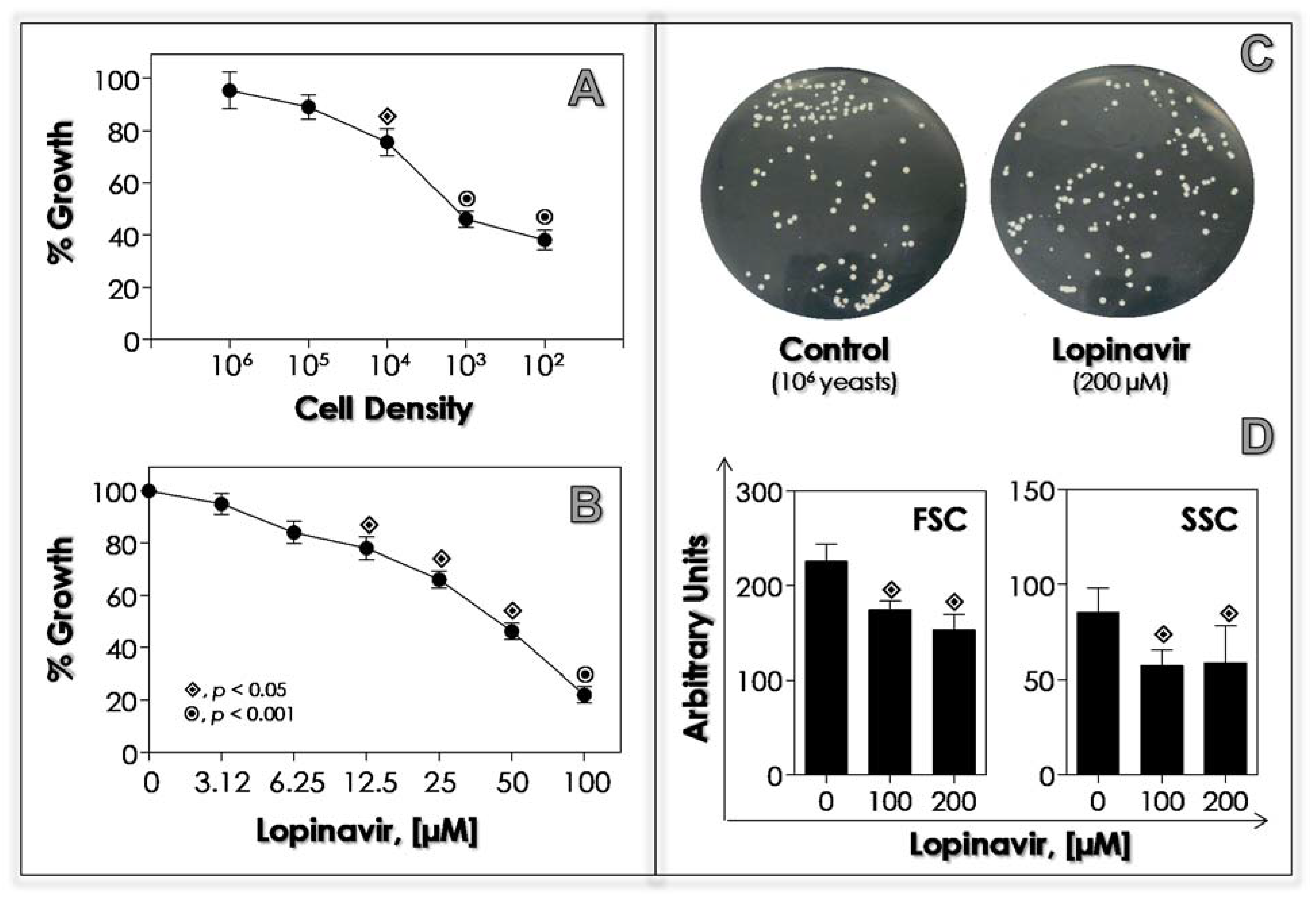
JoF | Free Full-Text | Repositioning Lopinavir, an HIV Protease Inhibitor, as a Promising Antifungal Drug: Lessons Learned from Candida albicans—In Silico, In Vitro and In Vivo Approaches

PDF) Kinin release from human kininogen by 10 aspartic proteases produced by pathogenic yeast Candida albicans

Role of NAPDH oxidase in Sap-induced netosis. Neutrophils (2.2 × 10 5... | Download Scientific Diagram

JoF | Free Full-Text | Repositioning Lopinavir, an HIV Protease Inhibitor, as a Promising Antifungal Drug: Lessons Learned from Candida albicans—In Silico, In Vitro and In Vivo Approaches
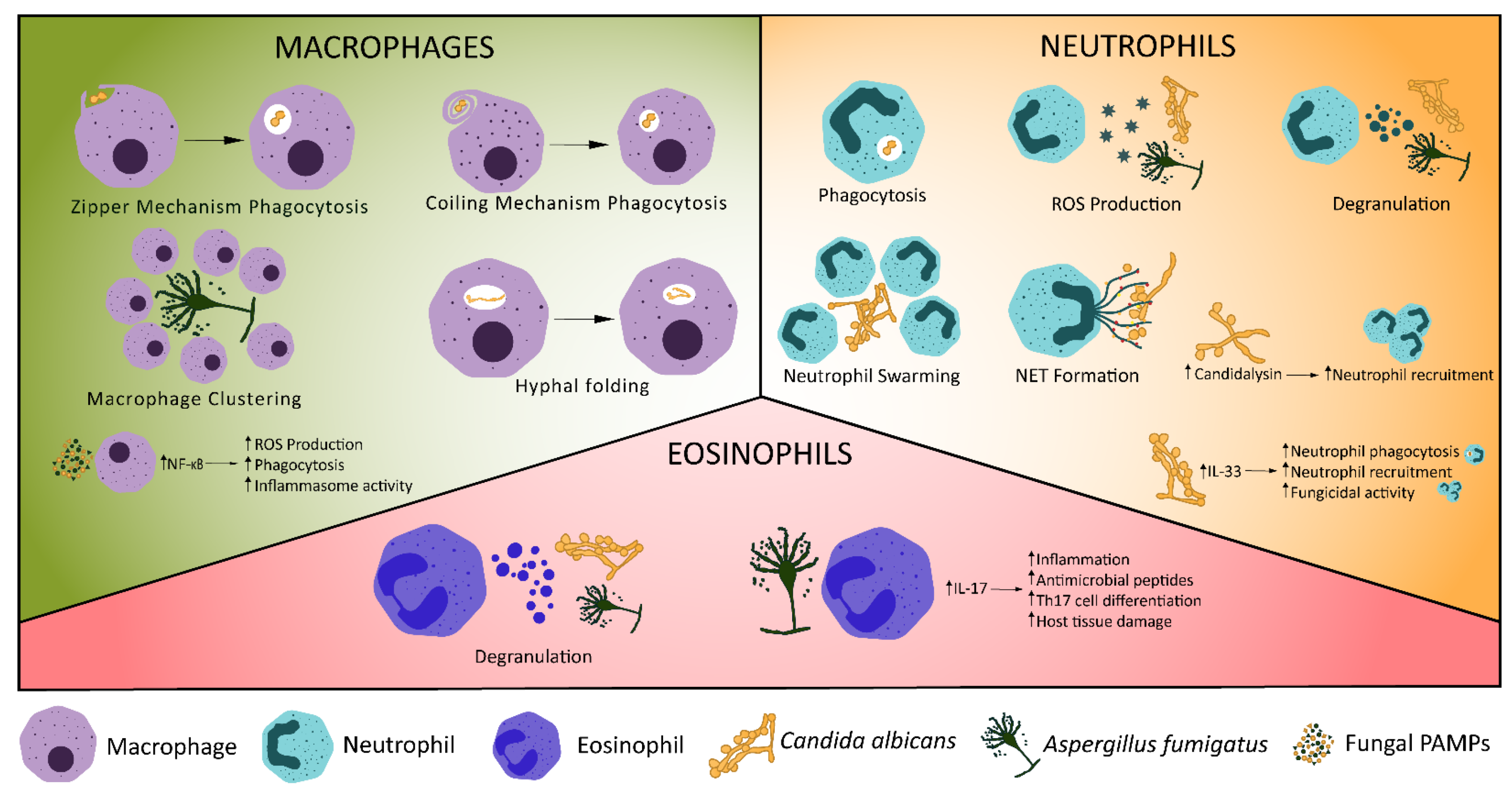
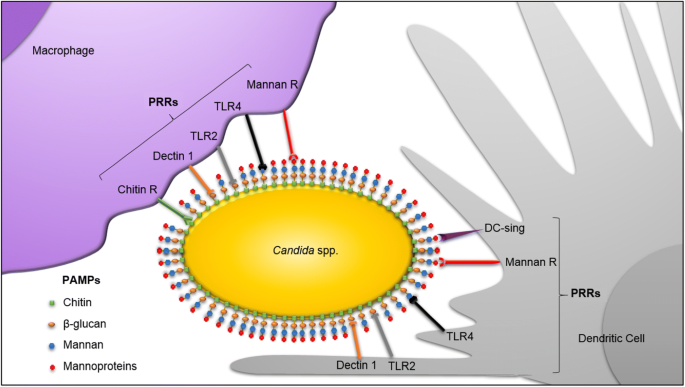
JoF | Free Full-Text | Candida albicans—The Virulence Factors and Clinical Manifestations of Infection
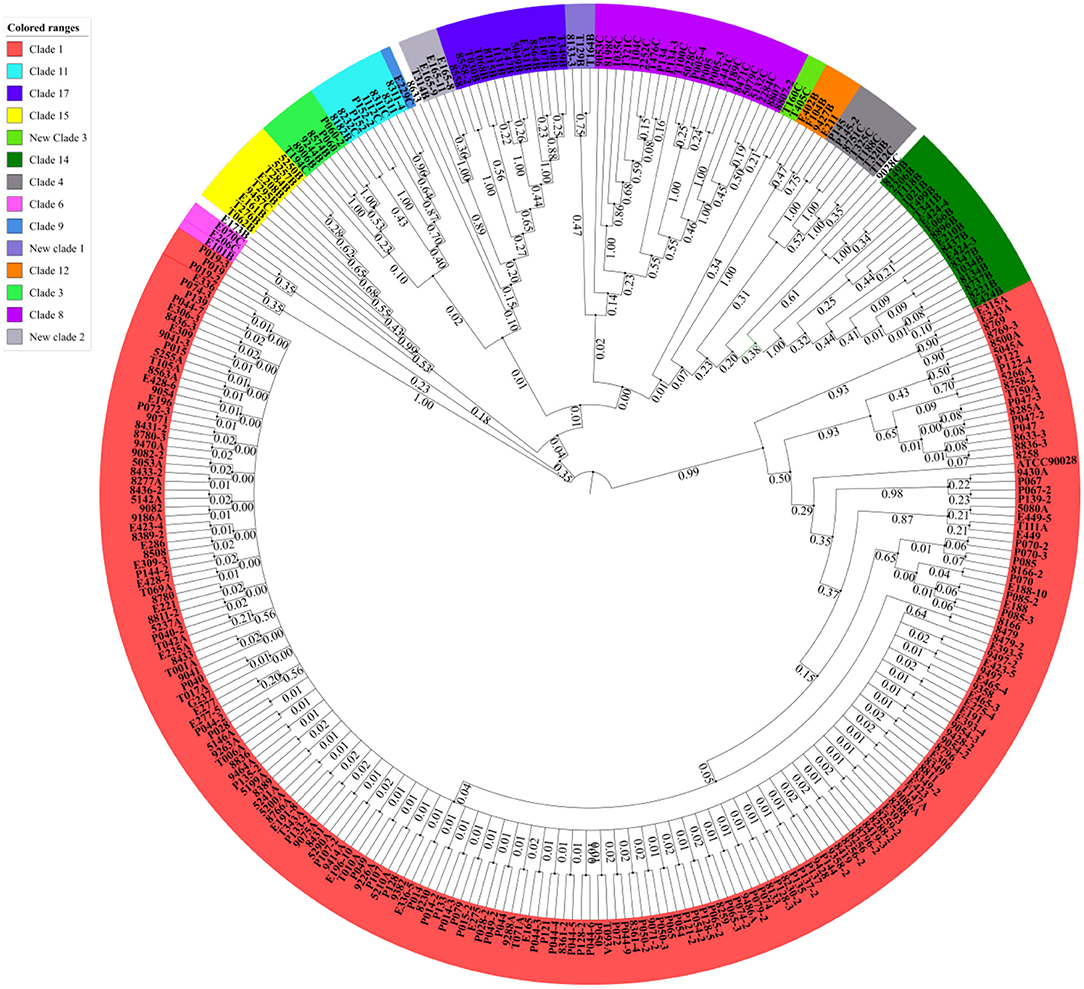
Frontiers | Candida albicans Multilocus Sequence Typing Clade I Contributes to the Clinical Phenotype of Vulvovaginal Candidiasis Patients

Frontiers | Aspartic Proteases and Major Cell Wall Components in Candida albicans Trigger the Release of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps

Aspartic Proteases and Major Cell Wall Components in Candida albicans Trigger the Release of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps | Semantic Scholar
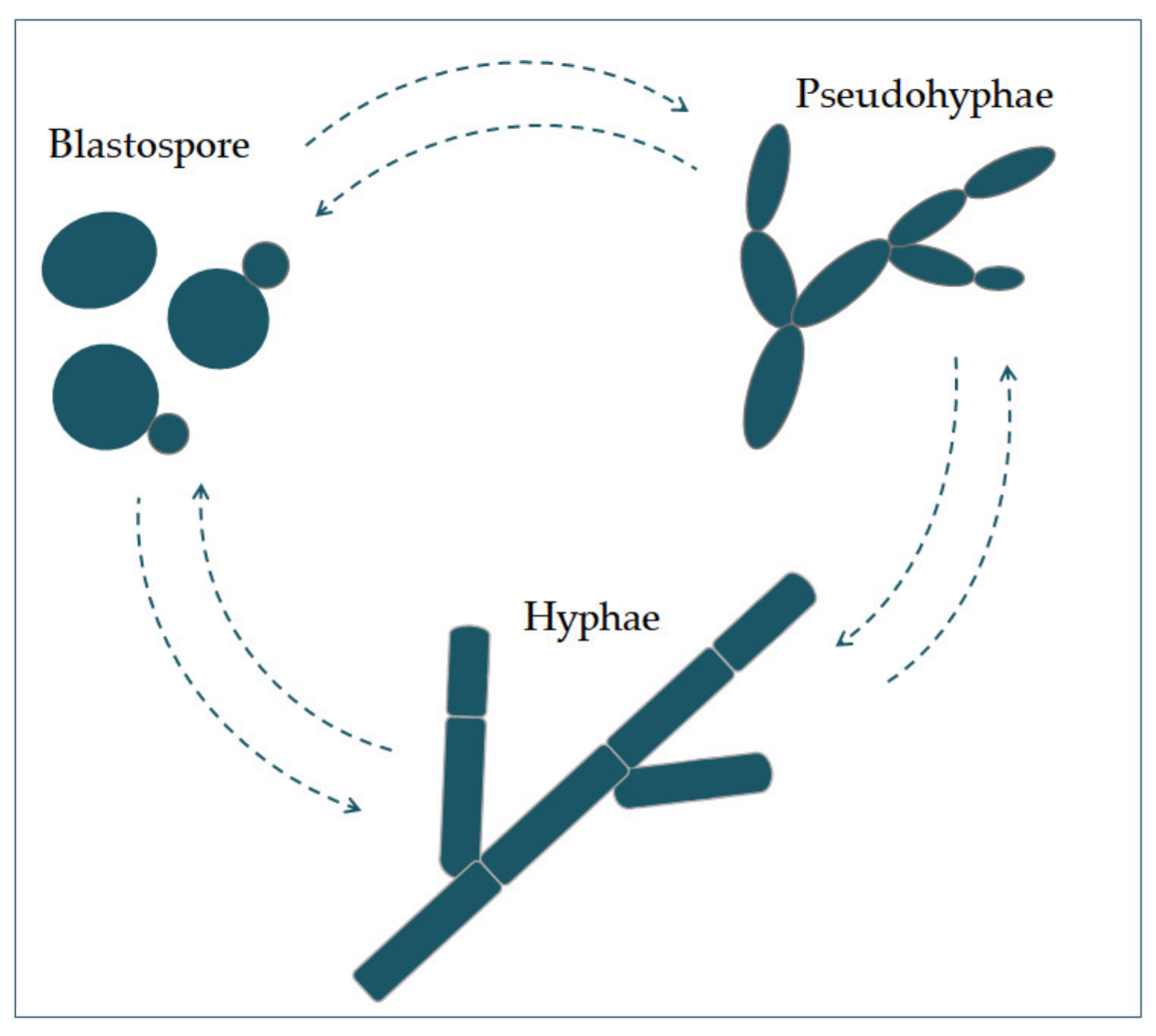
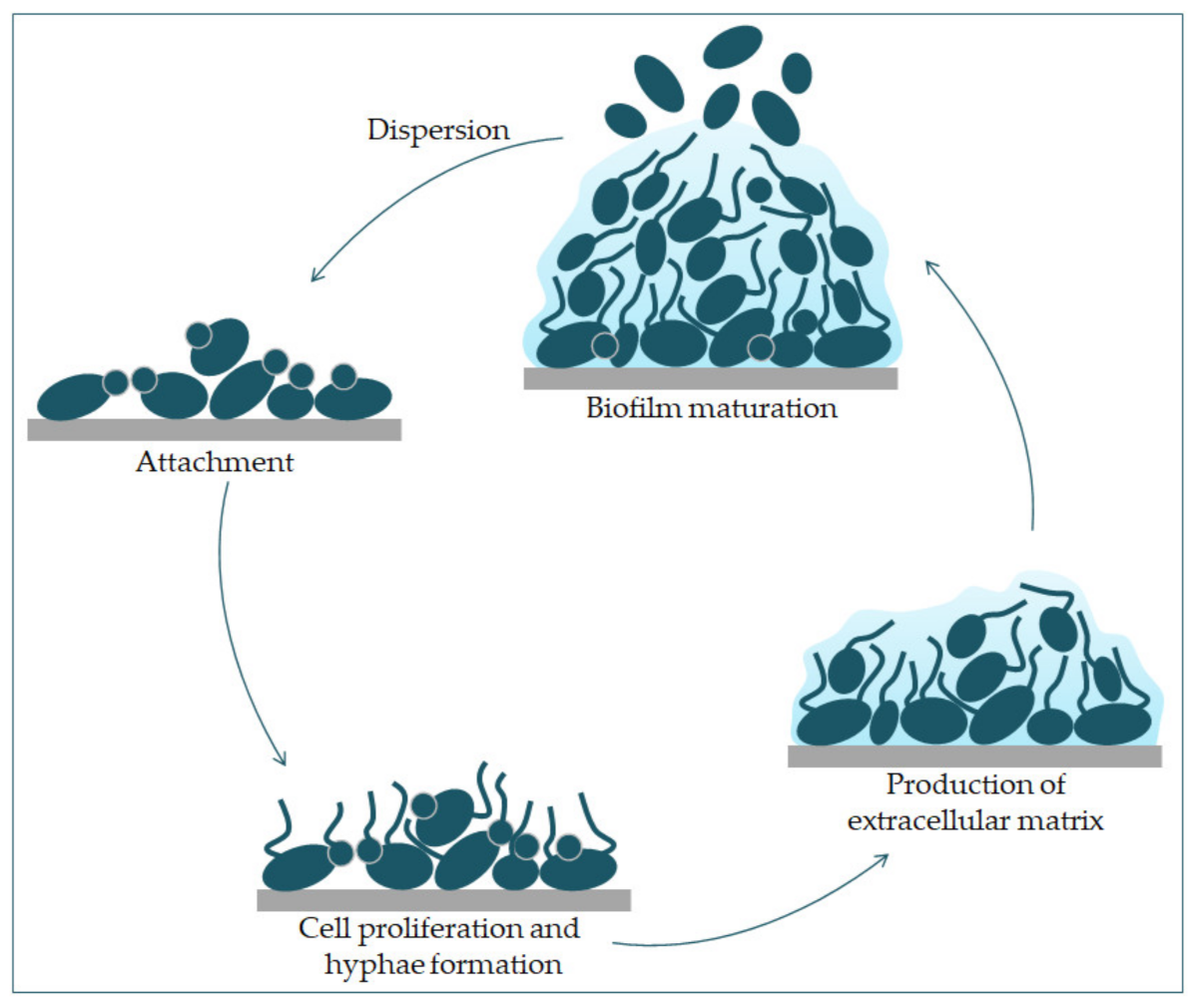
JoF | Free Full-Text | Candida albicans—The Virulence Factors and Clinical Manifestations of Infection

PDF) Genetic Variability of Candida albicans Sap8 Propeptide in Isolates from Different Types of Infection

Aspartic Proteases and Major Cell Wall Components in Candida albicans Trigger the Release of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps | Semantic Scholar

Proteomics Unravels Extracellular Vesicles as Carriers of Classical Cytoplasmic Proteins in Candida albicans | Journal of Proteome Research
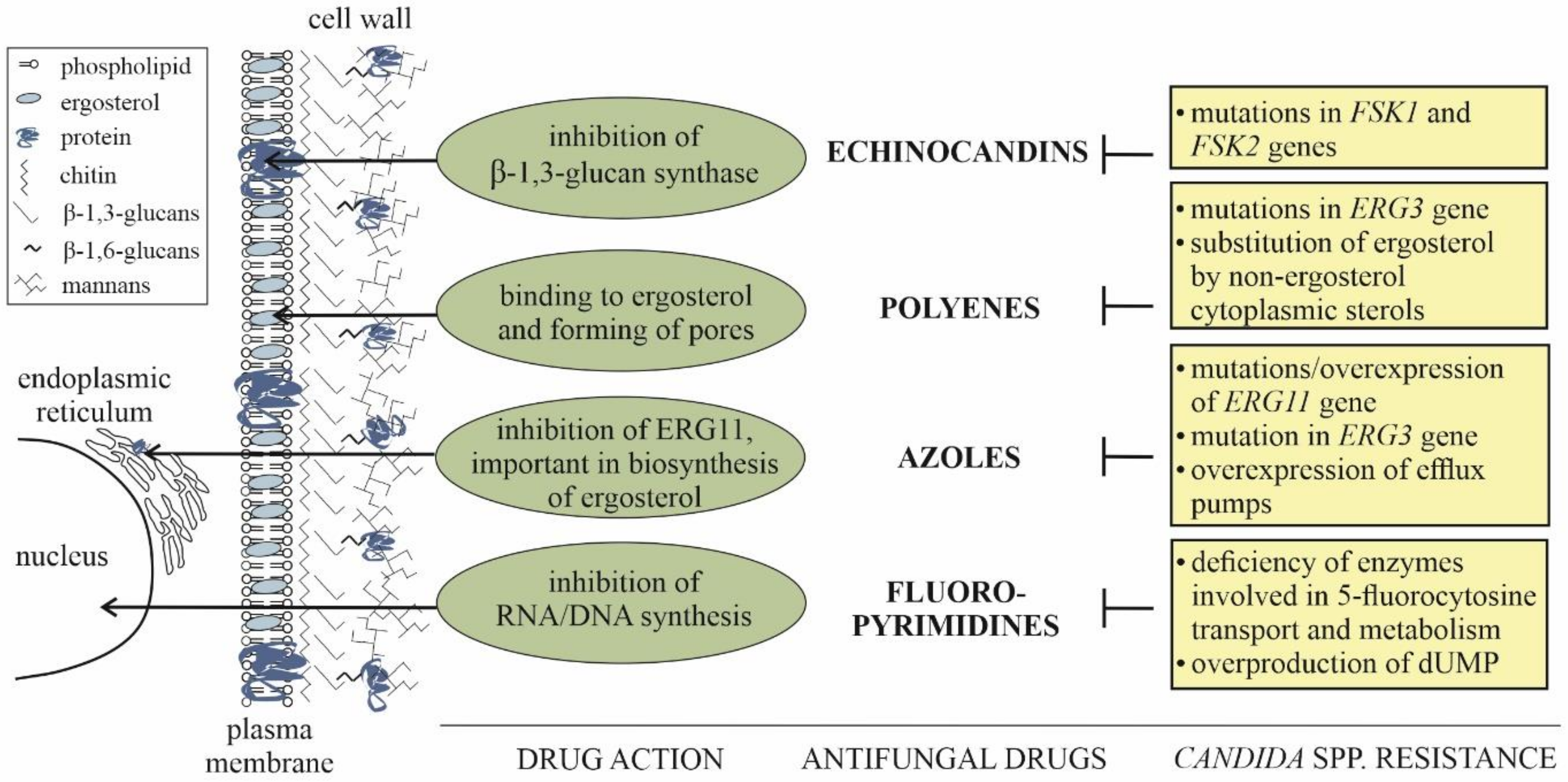
IJMS | Free Full-Text | Plant-Derived Substances in the Fight Against Infections Caused by Candida Species

Inactivation of LL-37 during the interplay between C. albicans cells... | Download Scientific Diagram
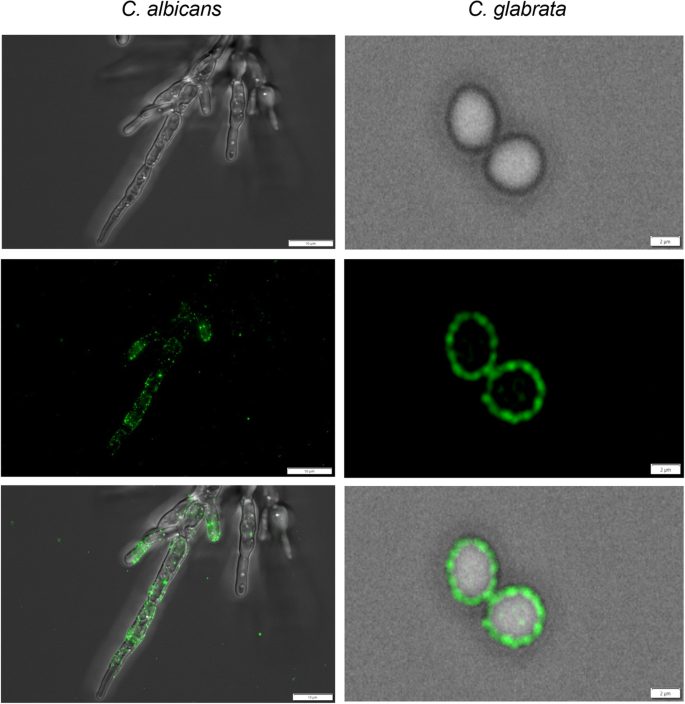
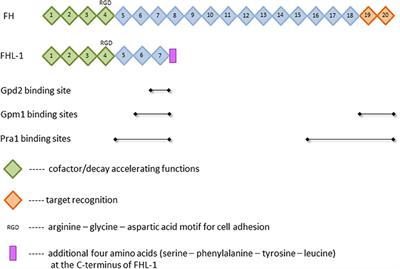
Candida albicans and Candida glabrata triosephosphate isomerase – a moonlighting protein that can be exposed on the candidal cell surface and bind to human extracellular matrix proteins | BMC Microbiology | Full Text

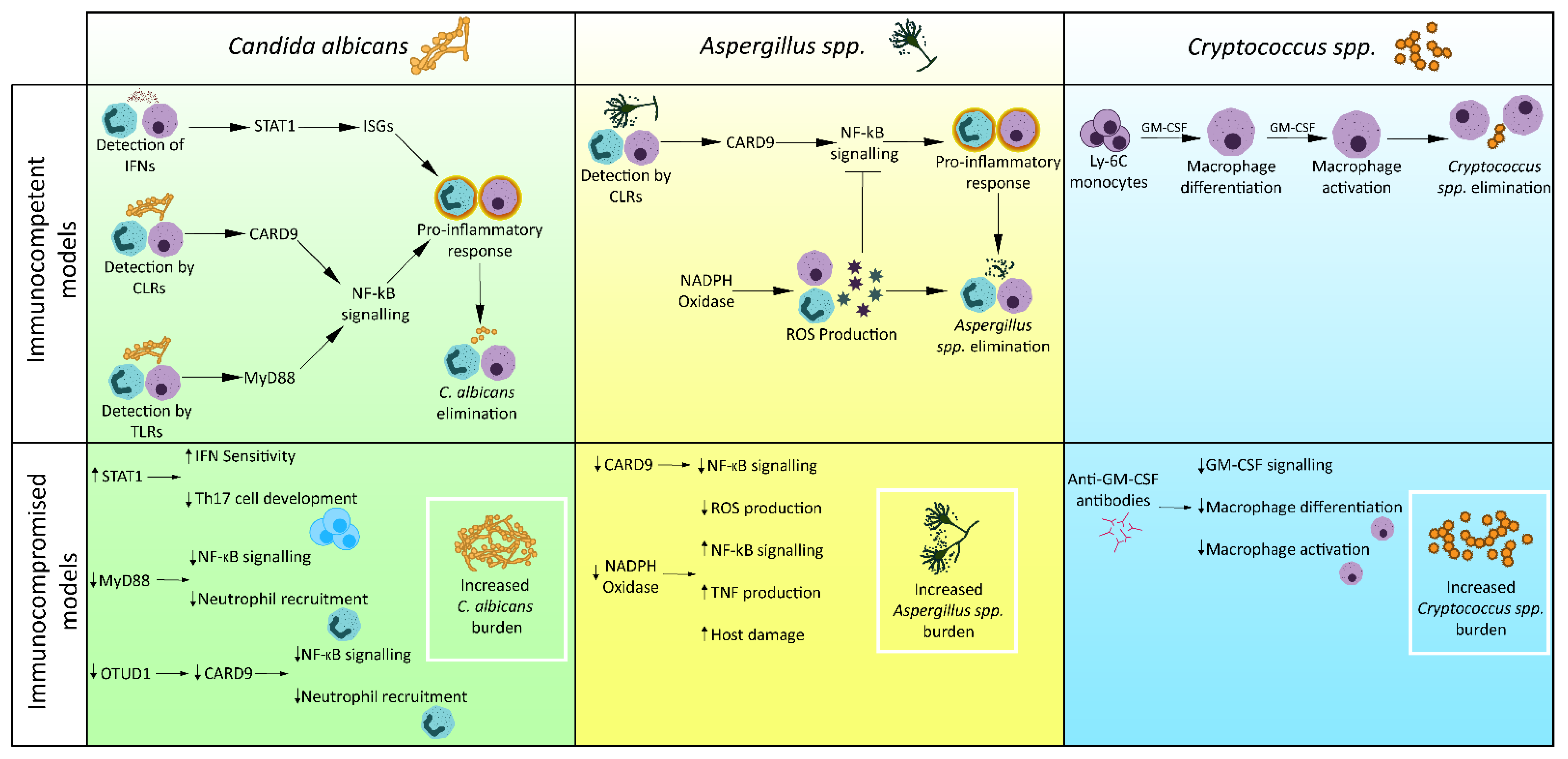
Full article: “Candida Albicans Interactions With The Host: Crossing The Intestinal Epithelial Barrier”