
Nickel transition metal Chemistry nickel(II) Ni2+ complex ions ligand substitution redox chemical reactions principal oxidation states +2 +3 GCE AS A2 IB A level inorganic chemistry revision notes
![The complex `[NiCl_(4)]^(2-)` has tetrahedral geometry while `[Ni(CN)_(4)]^(2-)` has square planar - YouTube The complex `[NiCl_(4)]^(2-)` has tetrahedral geometry while `[Ni(CN)_(4)]^(2-)` has square planar - YouTube](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/JCDuVCjb-Uk/maxresdefault.jpg?sqp=-oaymwEmCIAKENAF8quKqQMa8AEB-AH-CYAC0AWKAgwIABABGGUgZShlMA8=&rs=AOn4CLABPYxM2ekkgRxLQOhhqKsuv5imwQ)
The complex `[NiCl_(4)]^(2-)` has tetrahedral geometry while `[Ni(CN)_(4)]^(2-)` has square planar - YouTube
Explain the Ni(CO)4 is tetrahedral but [Ni(CN)4]^2– is square planar. - Sarthaks eConnect | Largest Online Education Community
![NI(Cl)2(P(CH3)3)2] is a paramagnetic complex of Ni(II), Analgous Pd(II) complex is diamagnetic. How many geometrical isomers will be possible for Ni(II) and Pd(II) complexes? Also explain their magnetic behaviour. NI(Cl)2(P(CH3)3)2] is a paramagnetic complex of Ni(II), Analgous Pd(II) complex is diamagnetic. How many geometrical isomers will be possible for Ni(II) and Pd(II) complexes? Also explain their magnetic behaviour.](https://haygot.s3.amazonaws.com/questions/1292483_256043_ans_a5318a12ca584fbfa4350ce3909aa29c.jpg)
NI(Cl)2(P(CH3)3)2] is a paramagnetic complex of Ni(II), Analgous Pd(II) complex is diamagnetic. How many geometrical isomers will be possible for Ni(II) and Pd(II) complexes? Also explain their magnetic behaviour.
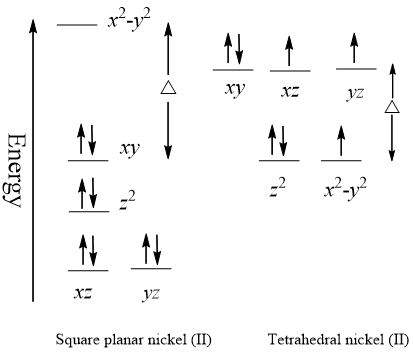
Solved: Chapter 20 Problem 120P Solution | Student Solutions Manual For General Chemistry 2nd Edition | Chegg.com
 complexes, R = Ph & (i)Pr revisited: experimental and theoretical analysis of interconversion pathways, structural preferences, and spin delocalization. | Semantic Scholar Figure 2 from Tetrahedral and square planar Ni[(SPR(2))(2)N](2) complexes, R = Ph & (i)Pr revisited: experimental and theoretical analysis of interconversion pathways, structural preferences, and spin delocalization. | Semantic Scholar](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/58b16eac82743c5c0d5832f5b3998d590ca529fb/6-Figure2-1.png)
Figure 2 from Tetrahedral and square planar Ni[(SPR(2))(2)N](2) complexes, R = Ph & (i)Pr revisited: experimental and theoretical analysis of interconversion pathways, structural preferences, and spin delocalization. | Semantic Scholar

Square Planar vs Tetrahedral Coordination in Diamagnetic Complexes of Nickel(II) Containing Two Bidentate π-Radical Monoanions | Inorganic Chemistry
![How would you account for the following? [Ni(CO)4] possesses tetrahedral geometry while [Ni(CN4)]^2 - is square planar. How would you account for the following? [Ni(CO)4] possesses tetrahedral geometry while [Ni(CN4)]^2 - is square planar.](https://haygot.s3.amazonaws.com/questions/1645912_1779345_ans_609fdfa33c594f688bfc4ddf925e04ff.png)
How would you account for the following? [Ni(CO)4] possesses tetrahedral geometry while [Ni(CN4)]^2 - is square planar.
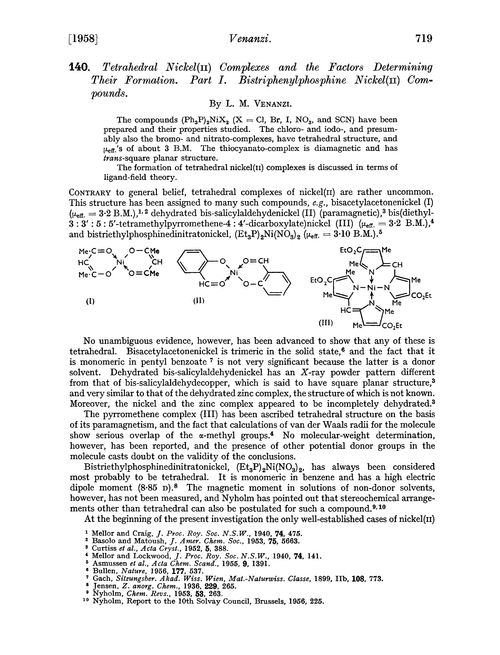
140. Tetrahedral nickel(II) complexes and the factors determining their formation. Part I. Bistriphenylphosphine nickel(II) compounds - Journal of the Chemical Society (Resumed) (RSC Publishing)
![The diamagnetic [Ni(CN)_4]^2- ion has square-planar geometry, and the paramagnetic [NiCl_4]^2- ion has tetrahedral geometry. Use crystal field splitting diagrams to explain the difference in the magne | Homework.Study.com The diamagnetic [Ni(CN)_4]^2- ion has square-planar geometry, and the paramagnetic [NiCl_4]^2- ion has tetrahedral geometry. Use crystal field splitting diagrams to explain the difference in the magne | Homework.Study.com](https://homework.study.com/cimages/multimages/16/cms53022462554618608855.jpg)
The diamagnetic [Ni(CN)_4]^2- ion has square-planar geometry, and the paramagnetic [NiCl_4]^2- ion has tetrahedral geometry. Use crystal field splitting diagrams to explain the difference in the magne | Homework.Study.com
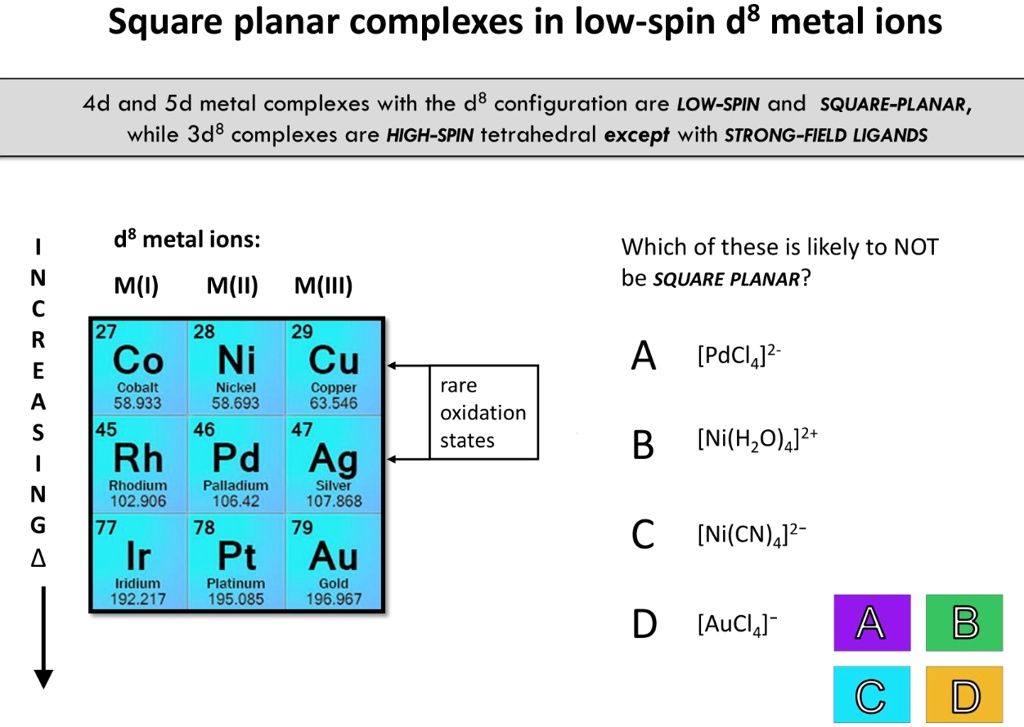
SOLVED: Square planar complexes in low-spin d8 metal ions 4d and Sd metal complexes with the d8 configuration are LOW-SPIN and SQUARE-PLANAR, while 3d8 complexes are HIGH-SPIN tetrahedral except with STRONG-FIELD LIGANDS
![Tetrahedral and Square Planar Ni[(SPR2)2N]2 complexes, R = Ph & iPr Revisited: Experimental and Theoretical Analysis of Interconversion Pathways, Structural Preferences, and Spin Delocalization | Inorganic Chemistry Tetrahedral and Square Planar Ni[(SPR2)2N]2 complexes, R = Ph & iPr Revisited: Experimental and Theoretical Analysis of Interconversion Pathways, Structural Preferences, and Spin Delocalization | Inorganic Chemistry](https://pubs.acs.org/cms/10.1021/ic100163g/asset/images/ic100163g.social.jpeg_v03)
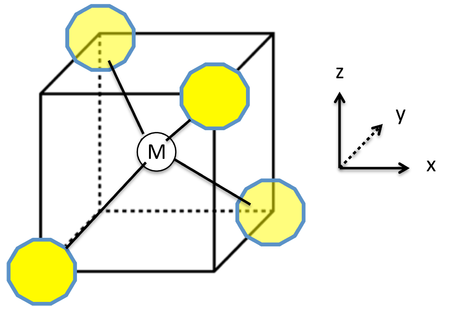

![Hybridization-Ni(CO)4 | [Ni(CN)4]2-| [Ni(Cl)4]2- | Structure-Parmagnetic-Diamagnetic-Examples-dsp2 Hybridization-Ni(CO)4 | [Ni(CN)4]2-| [Ni(Cl)4]2- | Structure-Parmagnetic-Diamagnetic-Examples-dsp2](http://www.adichemistry.com/jee/qb/coordination-chemistry/1/q1-2.png)

![coordination compounds - Why is Ni[(PPh₃)₂Cl₂] tetrahedral? - Chemistry Stack Exchange coordination compounds - Why is Ni[(PPh₃)₂Cl₂] tetrahedral? - Chemistry Stack Exchange](https://i.stack.imgur.com/AD72m.png)
