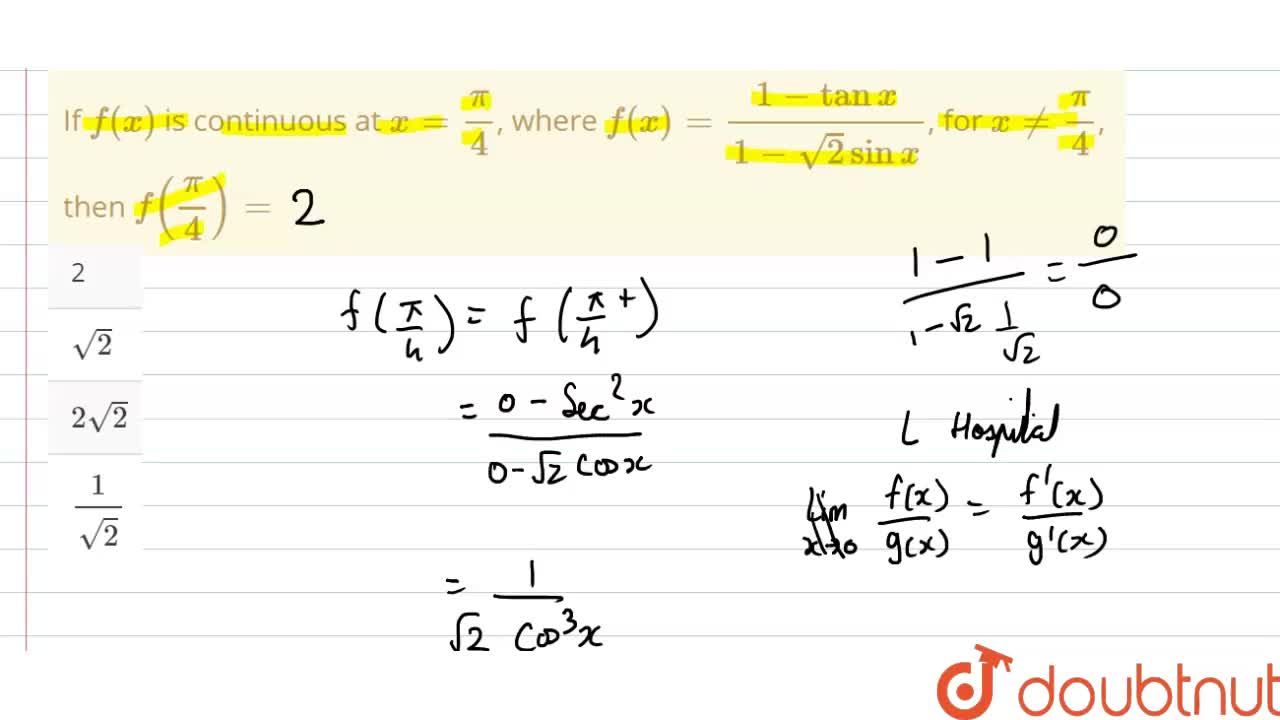
If `f(x)` is continuous at `x=pi/4`, where `f(x)=(1-tanx)/(1-sqrt(2)sin x)`, for `x!= pi/4`, then - YouTube

Express the arc length of y = sin x from x = 0 to x = pi as an integral. Then use calculator to approximate this value. | Homework.Study.com
![The period of sinpi[x]/12 + cospi[x]/4 + tanpi[x]/3 where [x] represents the greatest integer less than or equal to x is The period of sinpi[x]/12 + cospi[x]/4 + tanpi[x]/3 where [x] represents the greatest integer less than or equal to x is](https://d1hhj0t1vdqi7c.cloudfront.net/v1/eU5pc0x2Zjhqb28=/sd/)
The period of sinpi[x]/12 + cospi[x]/4 + tanpi[x]/3 where [x] represents the greatest integer less than or equal to x is

Graph the function f(x) = \cos^{2}x \sin x and use the graph to guess the value of the integral \int_{0}^{2\pi} f(x) dx. Then evaluate the integral to confirm your guess. | Homework.Study.com

Sketch the region enclosed by the given curves and compute its area. y = tan x, y = 2sin x, -pi/3 less than or equal to x less than or equal to






![The number of solutions of the equation 1 + sin^4x = cos^23x, x∈ [ - 5pi2, 5pi2 ] is? The number of solutions of the equation 1 + sin^4x = cos^23x, x∈ [ - 5pi2, 5pi2 ] is?](https://haygot.s3.amazonaws.com/questions/1493551_1665197_ans_f6a00f3a652f4aad8e28e1b0fda724df.jpg)